Tutorial Assistant: Generate technology tutorial
Role Introduction
Function Description
Generate a technical tutorial document based on a single sentence input, with support for custom languages.
Design Concept
The design approach involves using the LLM (Large Language Model) to initially generate the tutorial's outline. Then, the outline is divided into sections based on secondary headings. For each section, detailed content is generated according to the headings. Finally, the titles and content are concatenated. The use of sections addresses the limitation of long text in the LLM model.
Source Code
Role Definition
Define the role class, inheriting from the
Rolebase class, and override the__init__initialization method. The__init__method must include the parametersname,profile,goal, andconstraints. The first line of code usessuper().__init__(name, profile, goal, constraints)to call the constructor of the parent class, initializing theRole. Useself._init_actions([WriteDirectory(language=language)])to add initialactionandstates. Here, the write directory action is added initially. Additionally, custom parameters can be defined; here, thelanguageparameter is added to support custom languages. Useself._set_react_mode(react_mode="by_order")to set the execution order of actions in_init_actionsto sequential.pythonclass TutorialAssistant(Role): """Tutorial assistant, input one sentence to generate a tutorial document in markup format. Args: name: The name of the role. profile: The role profile description. goal: The goal of the role. constraints: Constraints or requirements for the role. language: The language in which the tutorial documents will be generated. """ def __init__( self, name: str = "Stitch", profile: str = "Tutorial Assistant", goal: str = "Generate tutorial documents", constraints: str = "Strictly follow Markdown's syntax, with neat and standardized layout", language: str = "Chinese", ): super().__init__(name, profile, goal, constraints) self._init_actions([WriteDirectory(language=language)]) self.topic = "" self.main_title = "" self.total_content = "" self.language = language self._set_react_mode(react_mode="by_order")class TutorialAssistant(Role): """Tutorial assistant, input one sentence to generate a tutorial document in markup format. Args: name: The name of the role. profile: The role profile description. goal: The goal of the role. constraints: Constraints or requirements for the role. language: The language in which the tutorial documents will be generated. """ def __init__( self, name: str = "Stitch", profile: str = "Tutorial Assistant", goal: str = "Generate tutorial documents", constraints: str = "Strictly follow Markdown's syntax, with neat and standardized layout", language: str = "Chinese", ): super().__init__(name, profile, goal, constraints) self._init_actions([WriteDirectory(language=language)]) self.topic = "" self.main_title = "" self.total_content = "" self.language = language self._set_react_mode(react_mode="by_order")Override the
reactmethod. Useawait super().react()to call thereactmethod of theRolebase class. According to thereact_mode="by_order"set in the__init__method, execute eachactioninstatesin order. The purpose of overriding here is to perform final operations after completing all actions, i.e., writing the concatenated tutorial content into amarkdownfile.pythonasync def react(self) -> Message: msg = await super().react() root_path = TUTORIAL_PATH / datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S") await File.write(root_path, f"{self.main_title}.md", self.total_content.encode('utf-8')) return msgasync def react(self) -> Message: msg = await super().react() root_path = TUTORIAL_PATH / datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S") await File.write(root_path, f"{self.main_title}.md", self.total_content.encode('utf-8')) return msgOverride the
_actmethod. The_actmethod is responsible for executing theaction. Usetodo = self._rc.todoto get the nextactionto be executed from the context, and then execute therunmethod of theaction. Here, it first obtains the tutorial directory structure throughWriteDirectory, then chunks the directory, generates aWriteContentaction for each chunk, and initializes the newly added action. Here, callingawait super().react()again is to execute all the newly addedWriteContentactions from the beginning. The result of each action is used to generate a messageMessage(content=resp, role=self.profile), which can be placed in the context memoryself._rc.memory. This role does not need to be stored.pythonasync def _act(self) -> Message: todo = self._rc.todo if type(todo) is WriteDirectory: msg = self._rc.memory.get(k=1)[0] self.topic = msg.content resp = await todo.run(topic=self.topic) logger.info(resp) await self._handle_directory(resp) return await super().react() resp = await todo.run(topic=self.topic) logger.info(resp) if self.total_content != "": self.total_content += "\n\n\n" self.total_content += resp return Message(content=resp, role=self.profile) async def _handle_directory(self, titles: Dict) -> Message: """Handle the directories for the tutorial document. Args: titles: A dictionary containing the titles and directory structure, such as {"title": "xxx", "directory": [{"dir 1": ["sub dir 1", "sub dir 2"]}]} Returns: A message containing information about the directory. """ self.main_title = titles.get("title") directory = f"{self.main_title}\n" self.total_content += f"# {self.main_title}" actions = list() for first_dir in titles.get("directory"): actions.append(WriteContent(language=self.language, directory=first_dir)) key = list(first_dir.keys())[0] directory += f"- {key}\n" for second_dir in first_dir[key]: directory += f" - {second_dir}\n" self._init_actions(actions)async def _act(self) -> Message: todo = self._rc.todo if type(todo) is WriteDirectory: msg = self._rc.memory.get(k=1)[0] self.topic = msg.content resp = await todo.run(topic=self.topic) logger.info(resp) await self._handle_directory(resp) return await super().react() resp = await todo.run(topic=self.topic) logger.info(resp) if self.total_content != "": self.total_content += "\n\n\n" self.total_content += resp return Message(content=resp, role=self.profile) async def _handle_directory(self, titles: Dict) -> Message: """Handle the directories for the tutorial document. Args: titles: A dictionary containing the titles and directory structure, such as {"title": "xxx", "directory": [{"dir 1": ["sub dir 1", "sub dir 2"]}]} Returns: A message containing information about the directory. """ self.main_title = titles.get("title") directory = f"{self.main_title}\n" self.total_content += f"# {self.main_title}" actions = list() for first_dir in titles.get("directory"): actions.append(WriteContent(language=self.language, directory=first_dir)) key = list(first_dir.keys())[0] directory += f"- {key}\n" for second_dir in first_dir[key]: directory += f" - {second_dir}\n" self._init_actions(actions)
Action Definition
Define an
action, where eachactioncorresponds to aclassobject. Inherit from theActionbase class and override the__init__initialization method. The__init__method includes thenameparameter. The first line of code usessuper().__init__(name, *args, **kwargs)to call the constructor of the parent class, initializing theaction. Here, useargsandkwargsto pass other parameters to the parent class constructor, such ascontextandllm.python#!/usr/bin/env python3 # _*_ coding: utf-8 _*_ """ @Time : 2023/9/4 15:40:40 @Author : Stitch-z @File : tutorial_assistant.py @Describe : Actions of the tutorial assistant, including writing directories and document content. """ from typing import Dict from metagpt.actions import Action from metagpt.prompts.tutorial_assistant import DIRECTORY_PROMPT, CONTENT_PROMPT from metagpt.utils.common import OutputParser class WriteDirectory(Action): """Action class for writing tutorial directories. Args: name: The name of the action. language: The language to output, default is "Chinese". """ def __init__(self, name: str = "", language: str = "Chinese", *args, **kwargs): super().__init__(name, *args, **kwargs) self.language = language#!/usr/bin/env python3 # _*_ coding: utf-8 _*_ """ @Time : 2023/9/4 15:40:40 @Author : Stitch-z @File : tutorial_assistant.py @Describe : Actions of the tutorial assistant, including writing directories and document content. """ from typing import Dict from metagpt.actions import Action from metagpt.prompts.tutorial_assistant import DIRECTORY_PROMPT, CONTENT_PROMPT from metagpt.utils.common import OutputParser class WriteDirectory(Action): """Action class for writing tutorial directories. Args: name: The name of the action. language: The language to output, default is "Chinese". """ def __init__(self, name: str = "", language: str = "Chinese", *args, **kwargs): super().__init__(name, *args, **kwargs) self.language = languageOverride the
runmethod. Therunmethod is the main function foractionexecution, using theself._aask(prompt=prompt)method to query theLLMmodel.pythonasync def run(self, topic: str, *args, **kwargs) -> Dict: """Execute the action to generate a tutorial directory according to the topic. Args: topic: The tutorial topic. Returns: The tutorial directory information, including {"title": "xxx", "directory": [{"dir 1": ["sub dir 1", "sub dir 2"]}]}. """ prompt = DIRECTORY_PROMPT.format(topic=topic, language=self.language) resp = await self._aask(prompt=prompt) return OutputParser.extract_struct(resp, dict)async def run(self, topic: str, *args, **kwargs) -> Dict: """Execute the action to generate a tutorial directory according to the topic. Args: topic: The tutorial topic. Returns: The tutorial directory information, including {"title": "xxx", "directory": [{"dir 1": ["sub dir 1", "sub dir 2"]}]}. """ prompt = DIRECTORY_PROMPT.format(topic=topic, language=self.language) resp = await self._aask(prompt=prompt) return OutputParser.extract_struct(resp, dict)Other
actionwriting is similar.pythonclass WriteContent(Action): """Action class for writing tutorial content. Args: name: The name of the action. directory: The content to write. language: The language to output, default is "Chinese". """ def __init__(self, name: str = "", directory: str = "", language: str = "Chinese", *args, **kwargs): super().__init__(name, *args, **kwargs) self.language = language self.directory = directory async def run(self, topic: str, *args, **kwargs) -> str: """Execute the action to write document content according to the directory and topic. Args: topic: The tutorial topic. Returns: The written tutorial content. """ prompt = CONTENT_PROMPT.format(topic=topic, language=self.language, directory=self.directory) return await self._aask(prompt=prompt)class WriteContent(Action): """Action class for writing tutorial content. Args: name: The name of the action. directory: The content to write. language: The language to output, default is "Chinese". """ def __init__(self, name: str = "", directory: str = "", language: str = "Chinese", *args, **kwargs): super().__init__(name, *args, **kwargs) self.language = language self.directory = directory async def run(self, topic: str, *args, **kwargs) -> str: """Execute the action to write document content according to the directory and topic. Args: topic: The tutorial topic. Returns: The written tutorial content. """ prompt = CONTENT_PROMPT.format(topic=topic, language=self.language, directory=self.directory) return await self._aask(prompt=prompt)
Role Execution Results
Input Examples
MySQLTutorialRedisTutorialHiveTutorial
Execution Command Examples
Provide corresponding execution command examples.
Execution Results
The generated tutorial documents are located in the project's /data/tutorial_docx directory. Screenshots are provided below:
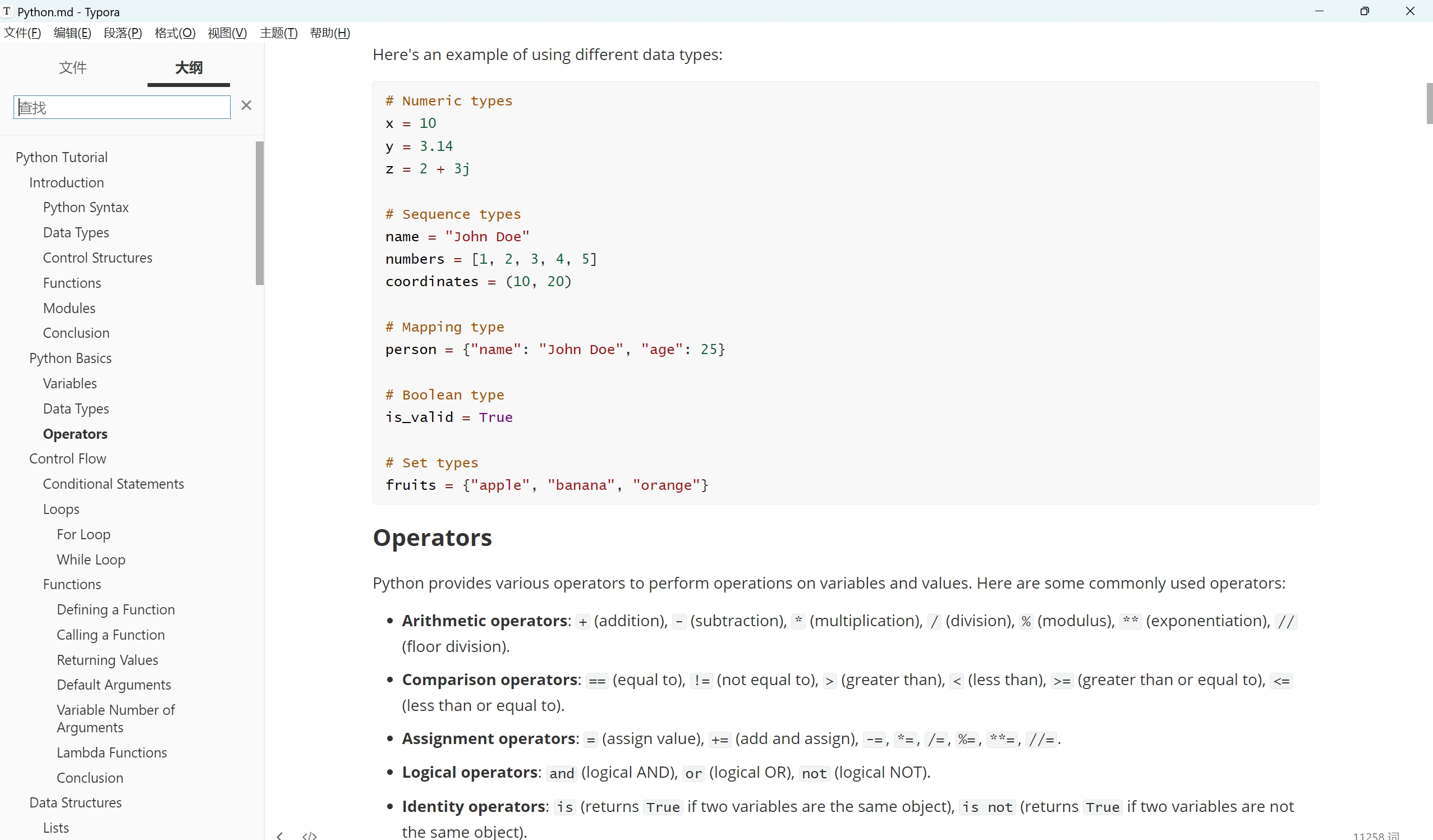
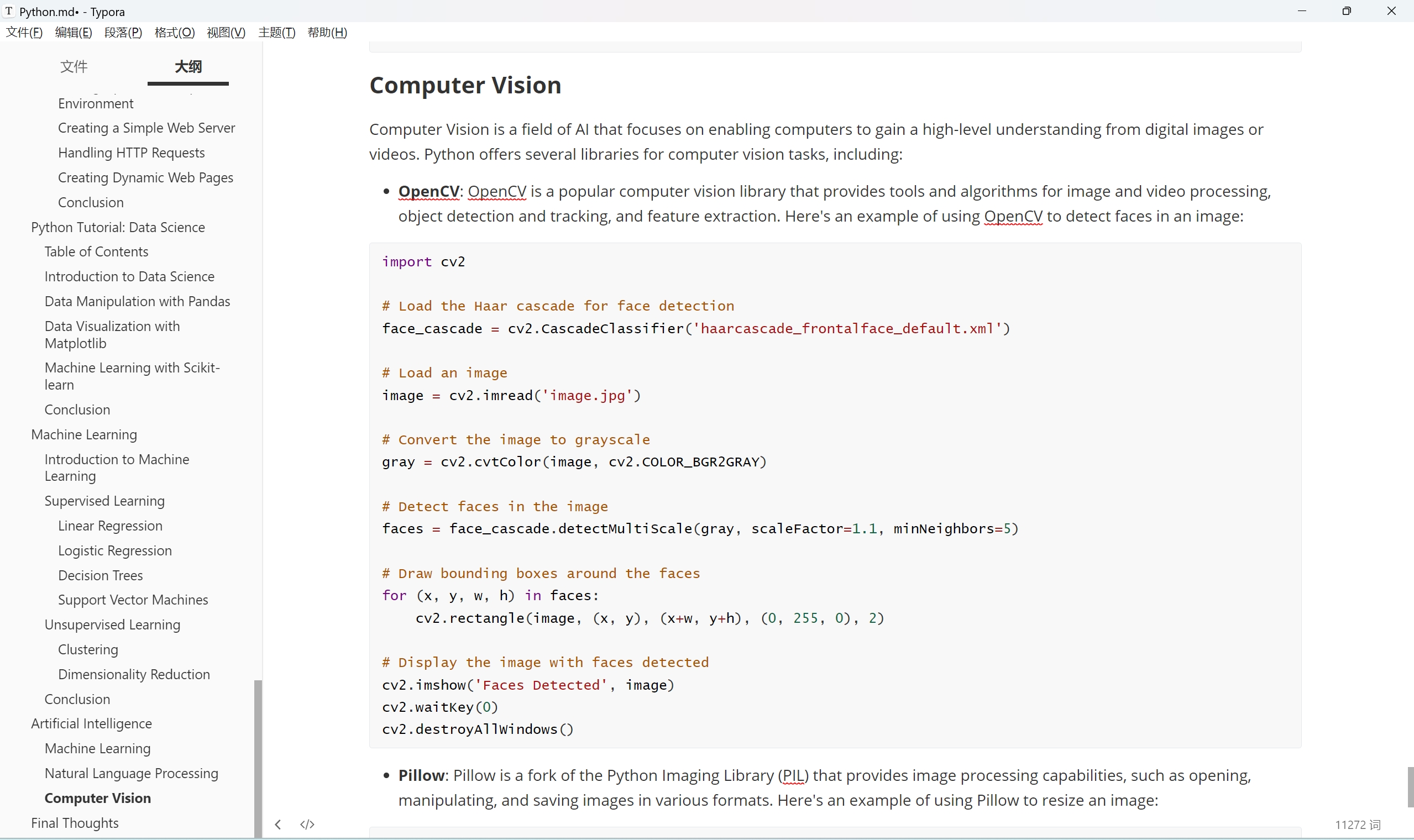
Note
This role currently does not support internet search capabilities. Content generation relies on data trained by the LLM large model.