思考与行动
在本教程之后,你将能够:
- 理解智能体在运行中如何思考与行动,以及每个阶段的用途
- 根据你的场景和需求,使用不同的反应模式
三种反应模式
在接收到来自环境的新观察后,智能体开始以恰当的思考和行动以回应这一观察。MetaGPT目前提供了两种定义这种思考和行动过程的方法,并将于近期补充第三种。
标准ReAct模式(默认)
先思考,再行动,直到角色认为是时候停止。这是ReAct论文中的标准思考-行动循环,即交替进行任务解决中的思考和行动,即 _think -> _act -> _think -> _act -> ...
每次在_think期间,Role将选择一个Action来响应当前的观察,并在_act阶段运行所选的Action。然后,操作输出将成为下一步在_think中再次使用的新观察。我们在_think中动态地使用LLM来选择动作,这使得该模式具有良好的通用性。
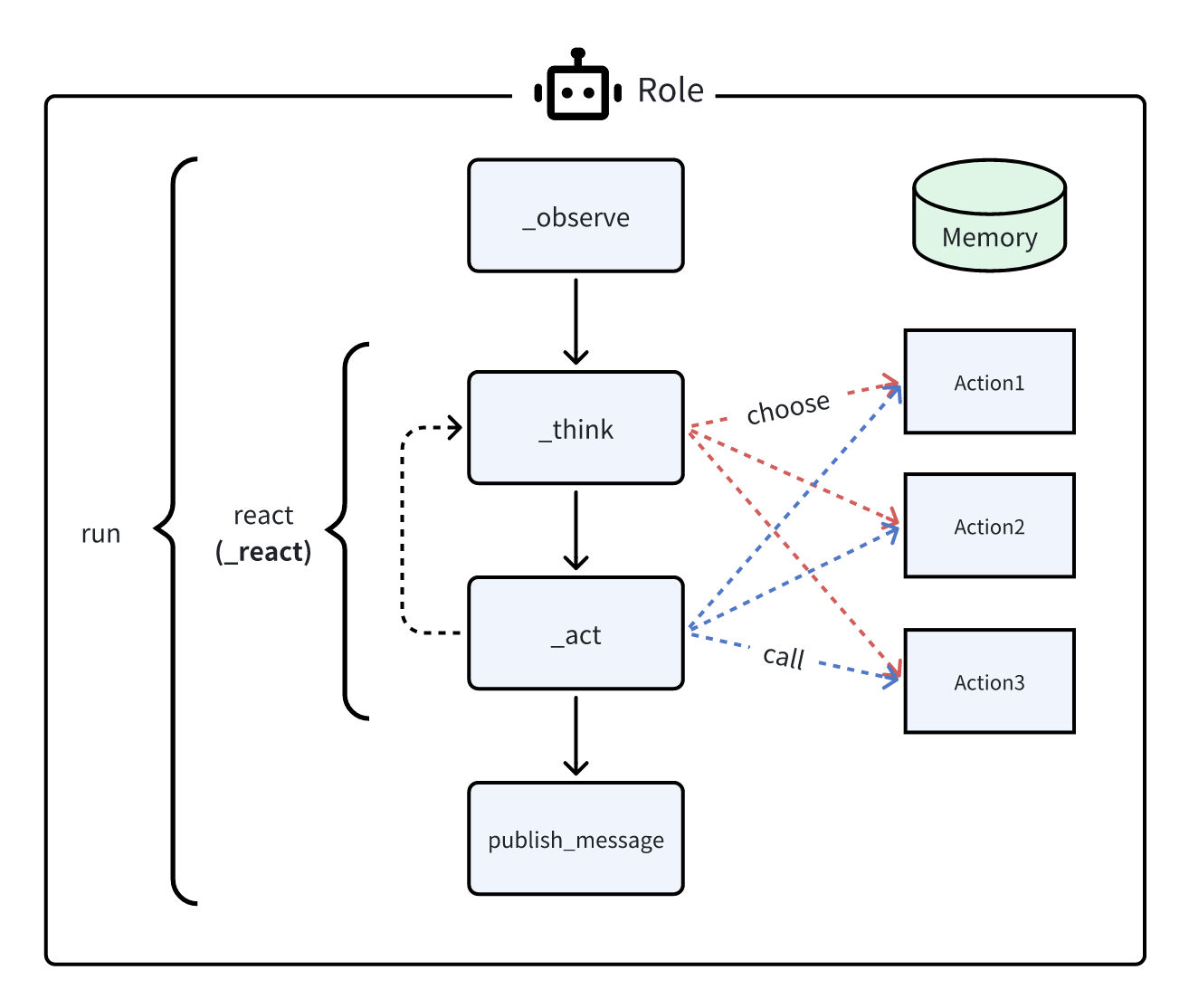
在MetaGPT中,Role默认设置为单次思考-行动循环的这种模式,因此你不需要指定任何内容。另一方面,如果你希望Role执行更多的思考-行动循环。在Role初始化时使用_set_react_mode。例如,下面的代码将允许3次思考-行动循环(_think或_act每个计为一次循环)
self._set_react_mode(react_mode="react", max_react_loop=6)self._set_react_mode(react_mode="react", max_react_loop=6)按顺序执行
每次按照_init_actions中定义的顺序执行可行的操作,即 _act (Action1) -> _act (Action2) -> _act (Action3) -> ...
这种模式适合于确定性的标准操作程序(SOP),在这种情况下我们确切地知道Role应该采取什么行动以及它们的顺序。使用这种模式,你只需要定义Action,框架将接管管道构建。
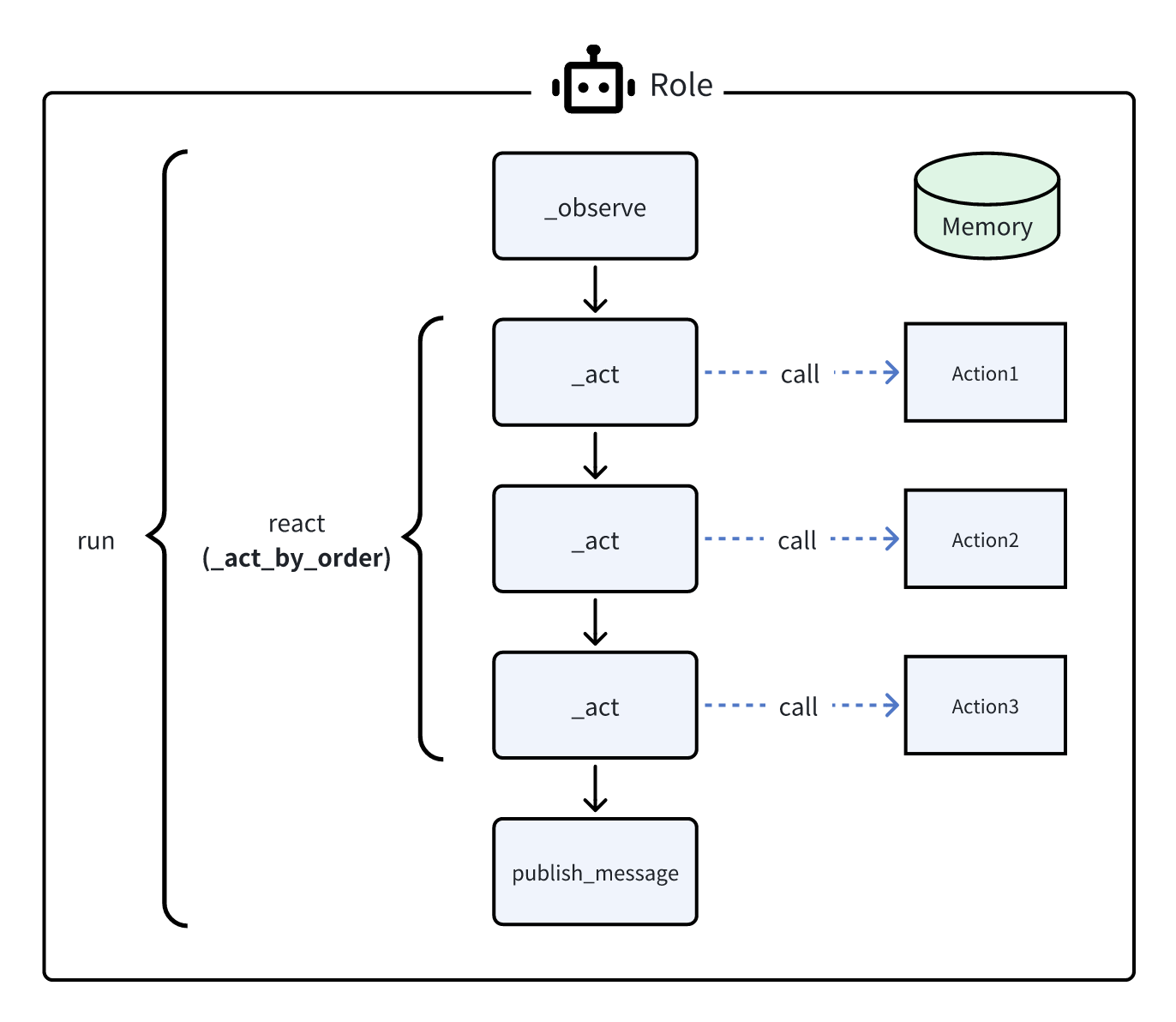
回想我们的智能体入门示例,通过指定self._set_react_mode(react_mode="by_order"),Role将首先执行SimpleWriteCode,然后执行SimpleRunCode。
class RunnableCoder(Role):
name: str = "Alice"
profile: str = "RunnableCoder"
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self._init_actions([SimpleWriteCode, SimpleRunCode])
self._set_react_mode(react_mode="by_order")
async def _act(self) -> Message:
...class RunnableCoder(Role):
name: str = "Alice"
profile: str = "RunnableCoder"
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self._init_actions([SimpleWriteCode, SimpleRunCode])
self._set_react_mode(react_mode="by_order")
async def _act(self) -> Message:
...规划与行动
提前制定计划,然后使用该计划指导一系列行动,即 _plan -> _act -> _act -> ...
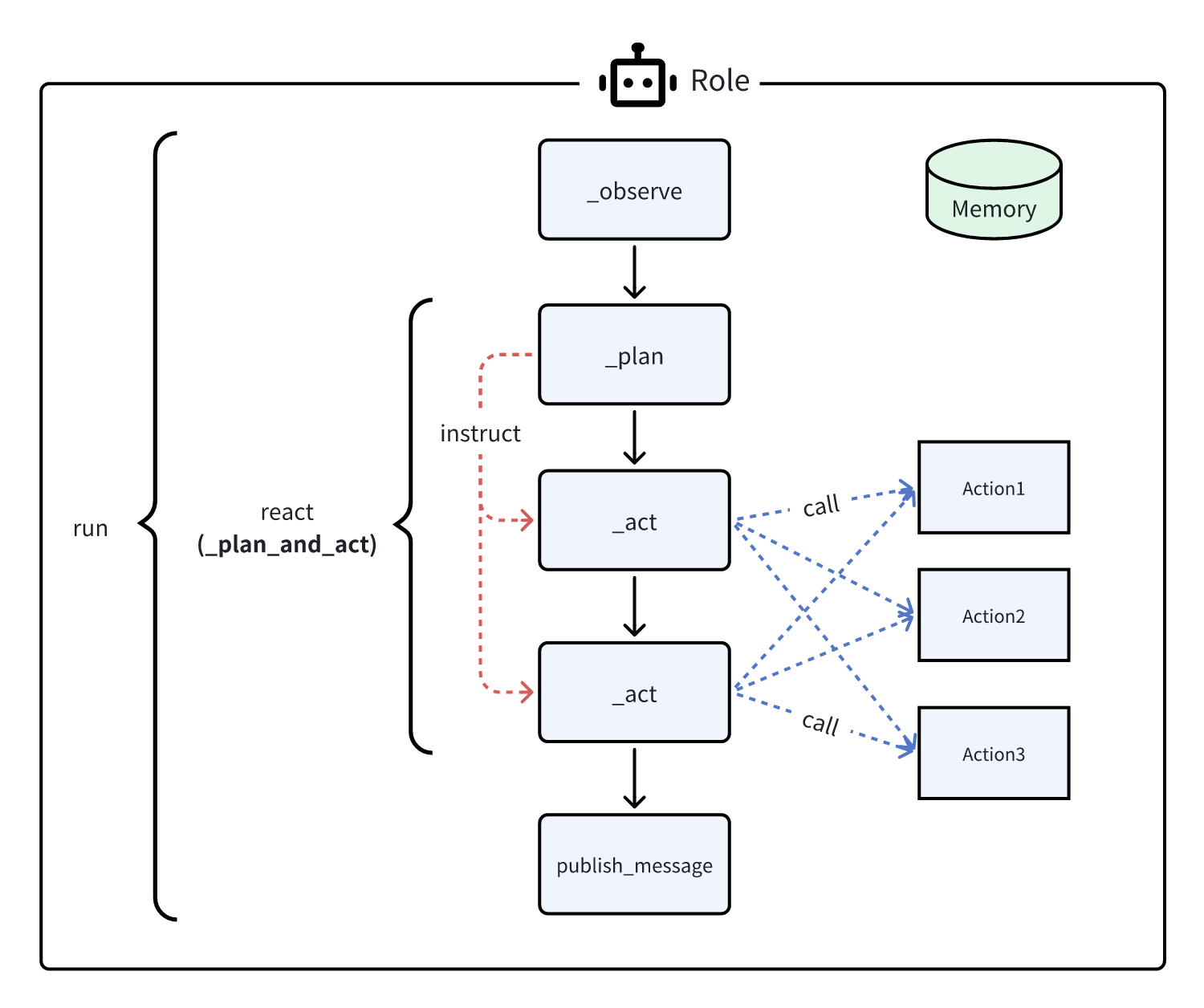
实现中,敬请期待